Be part dojicreates.com Development - Submit Your Java Tutorial
This page is currently under development.
Help Us Grow the Java Section!
Yes po, I know this is a very ambitious project and involves a
lot of work. Alam ko rin po na hindi ko kaya gawin ito mag-isa.
Kaya naisip ko, mas magiging masaya at meaningful ito kung
magiging bahagi kayo ng development na ito by submitting your
own content in PDF format.
What’s in it for you? Credit!
Yes po, I’m planning to include your name as credit in the title
itself, just like what you’ll see in the image below.
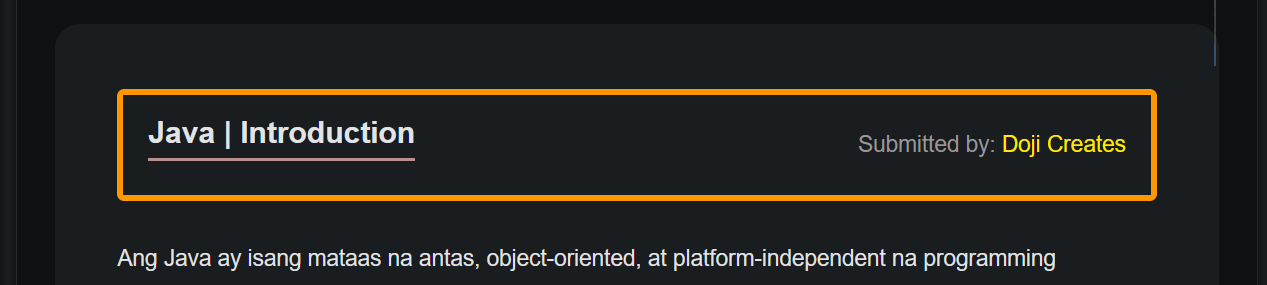
And hindi lang po basta simple credits lang, clickable link po
ito!
You can include a clean link like your social media account if
you want followers, or leave it blank if you prefer.
Your credits will remain as long as walang ibang submission na
mas mahusay ang explanation. So just because a topic already has
content doesn’t mean you can’t submit anymore. You’re always
welcome to try and submit your own version. With that said,
we’re now accepting your best works, send them in now!
Submission Guidelines
1. Content Requirements
- Write tutorials in Filipino (Tagalog)
- You can choose a topic from the scroll spy on the left side
- Focus on one Java topic per submission
- Include practical code examples with proper syntax
- Provide step-by-step explanations
- Show expected outputs
Code Example Format
import java.util.Scanner;
public class InputExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Ilagay ang iyong edad: ");
int edad = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Ang iyong edad ay: " + edad + " taon.");
sc.close();
}
}2. Recommended Java Topics
- Recommended: Blank topics like this have more higher chances of getting selected.
- Java Collections Framework
- Java Streams and Lambda
- OOP in Java
- Exception Handling
- File I/O
- JDBC
How to Submit
- Create a PDF of your Java tutorial following our guidelines
- Join our Facebook group
- Upload/Post your PDF with topic name and brief description on our FB Group
- Wait for feedback from our team
Example
Check our Java | Installing Java as a model for your submission.
Java Tutorial Submission Guidelines
Required Format for Java Submissions
Supervised by: dojicreatesThank you for your interest in submitting your own version of Java content to our platform! To ensure consistency and maintain high quality across all tutorials, please follow these detailed guidelines when preparing your submission.
Basic Page Structure
1. Tutorial Title
Always use this format: "Java Programming Tutorials: [Your Topic]"
Example: "Java Programming Tutorials: Access Modifiers"
2. Main Topic Header
Format your main heading as: Java [Your Topic]
Example: Java Access Modifiers
3. Introduction Paragraph
Provide a clear explanation of the concept with key terms in bold.
Example: "Ang access modifiers sa Java ay ginagamit upang kontrolin ang visibility o accessibility ng mga data members at member functions sa loob ng isang class. May apat na pangunahing access modifiers sa Java..."
Required Content Sections
1. Importance of the Topic
Section Header: Bakit Mahalaga ang [Your Topic]?
Content Format: List benefits with checkmarks ✔
Example:
- ✔ Pinapadali ang maintenance ng code.
- ✔ Pinoprotektahan ang data sa pamamagitan ng pagtatago ng internal details.
- ✔ Pinapababa ang complexity ng malalaking programa.
2. How the Concept Works
Section Header: Paano Gumagana ang [Your Topic]?
Content Format: Step-by-step explanation with ordered or unordered lists
Example:
Sa Java, may apat na paraan upang kontrolin ang access:
- ✔ Paggamit ng public access modifier para sa global access.
- ✔ Paggamit ng private para sa class-only access.
- ✔ Paggamit ng protected para sa package at subclass access.
- ✔ Paggamit ng default (no modifier) para sa package-level access.
3. Code Example
Section Header: Halimbawa ng [Your Topic]
Content Format: Complete, runnable Java code in a code block with Tagalog comments
Example:
package com.example;
public class BankAccount {
private double accountBalance; // Nakatago sa labas ng class
public void setBalance(double balance) {
accountBalance = balance;
}
public double getBalance() {
return accountBalance;
}
}4. Code Explanation
Section Header: Paliwanag ng Code
Content Format: Bullet points explaining each important part of the code
Example:
- `package com.example;` → Nagdedeklara ng package name para sa iyong Java class.
- `private double accountBalance;` → Itinatago ang balance upang hindi ito ma-access nang direkta.
- `public void setBalance(double balance);` → Public method upang itakda ang halaga ng balance.
- `public double getBalance();` → Public method upang makuha ang halaga ng balance.
5. Practical Application (Optional)
Section Header: [Variation] ng [Your Topic]
Content Format: Additional examples with short code snippets
Example:
Ang `protected` members ay hindi maaaring ma-access direkta, ngunit maaaring gamitin sa mga subclass:
package com.example;
public class Base {
protected int protectedVar;
}
public class Derived extends Base {
public void setVar(int value) {
protectedVar = value; // ✅ Pwede sa subclass
}
public int getVar() {
return protectedVar;
}
}6. Expected Output
Section Header: Expected Output:
Content Format: Plain text showing expected console output
Example:
Account Balance: 50007. Success Message
Content Format: Encouraging message with checkmark and celebration emoji
Example:
✅ Kapag lumabas ang "Account Balance: 5000" sa screen, matagumpay mong nai-run ang iyong Java access modifiers program! 🎉
Formatting Requirements
1. Text Formatting
- Use bold text for all important concepts and terms
- Use backticks for all code elements, function names, variables, and technical terms
- Place all section headers in bold
- Use consistent spacing between sections (one blank line minimum)
2. Code Blocks
- Every code example must be properly indented (4 spaces or 1 tab)
- All code must be runnable and error-free
- Add helpful comments in Tagalog to explain complex parts
- Include proper package declarations for all Java classes
- Follow Java naming conventions (camelCase for methods and variables, PascalCase for classes)
3. Visual Elements
- Use tables for comparing related concepts (e.g., access modifiers comparison)
- Use ordered lists for sequential steps or processes
- Use unordered lists for non-sequential items or options
- Use checkmarks (✔) to highlight positive points or key features
4. Language Guidelines
- Write primary content in Tagalog for better local understanding
- Keep all technical terms in English and format them with backticks
- Use a friendly, encouraging tone throughout the tutorial
- Address the reader directly with second-person perspective (e.g., "mong", "mo")
- Explain complex concepts with simple, clear language
Code Example Guidelines
Example of Well-Formatted Java Code:
package com.example;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* Example class demonstrating access modifiers in Java
*/
public class Example {
public int publicVar; // Maaaring ma-access kahit saan
private int privateVar; // Maaaring ma-access lang sa loob ng class
protected int protectedVar; // Maaaring ma-access sa loob ng class, package, at sa mga subclass
int defaultVar; // Maaaring ma-access sa loob ng package lamang (default access)
/**
* Setter para sa private variable
*/
public void setPrivate(int value) {
privateVar = value;
}
/**
* Getter para sa private variable
*/
public int getPrivate() {
return privateVar;
}
/**
* Main method para sa sample run
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Example obj = new Example();
obj.publicVar = 10;
System.out.println("Public Variable: " + obj.publicVar);
obj.setPrivate(20);
System.out.println("Private Variable: " + obj.getPrivate());
}
}Important Java Code Formatting Rules:
- Include proper package declarations and imports
- Add JavaDoc comments for classes and methods
- Include meaningful white space for readability
- Add descriptive Tagalog comments for key operations
- Align related code elements when appropriate
- Break long lines for better readability (100-120 characters maximum)
- Maintain consistent naming conventions throughout code samples
- Include a `main` method for runnable examples when appropriate
Java-Specific Guidelines
1. Package Structure
- Always include package declarations at the top of your Java files
- Use domain-name-style package naming (e.g., `com.example`)
- Organize related classes in the same package
2. Java Platform Versions
- Specify the Java version your code is written for (e.g., Java 8, Java 11, Java 17)
- When using newer Java features, mention the minimum required version
- Avoid deprecated features and methods in your examples
3. Common Java Framework Examples
- If demonstrating frameworks (Spring, JavaFX, etc.), provide basic configuration files
- For servlet or web examples, include the necessary web.xml configuration
- For database examples, use JDBC or JPA with appropriate setup instructions
How to Submit Your Tutorial
- Prepare your content following all format guidelines above
- Test all code examples to ensure they compile and run correctly
- Format in HTML using the same structure as our existing tutorials
- Submit via email to doji.adds@gmail.com with subject line "Java Tutorial Submission: [Your Topic]"
- Or Submit via posting your version on our Facebook group: https://www.facebook.com/groups/cspinas
All submissions will be reviewed for technical accuracy, quality of explanation, and adherence to these formatting guidelines before publication. We may request revisions to ensure consistency with our platform standards.
By submitting content, you agree to allow dojicreates to publish and modify your work as needed while maintaining attribution to you as the original author.